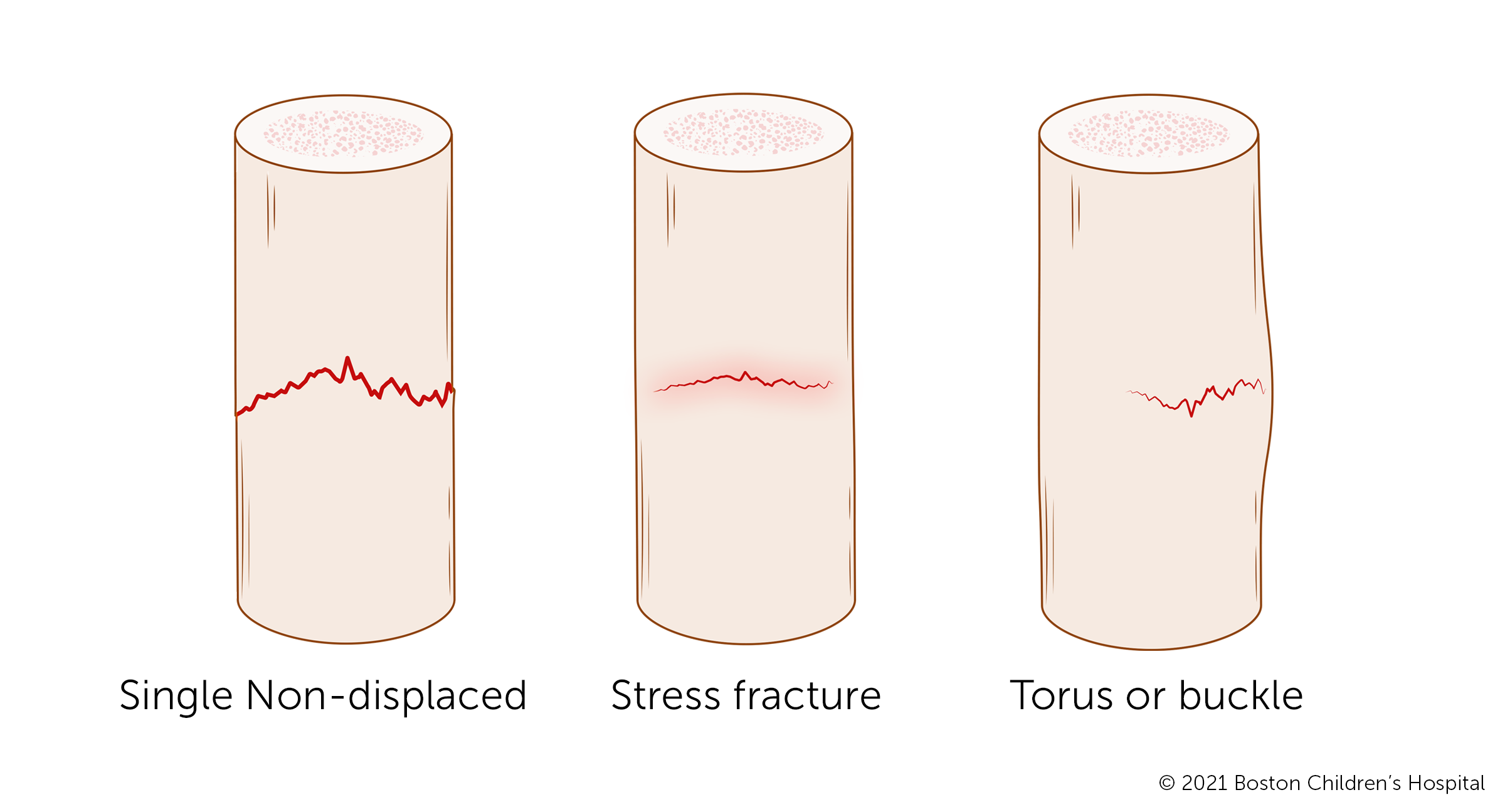
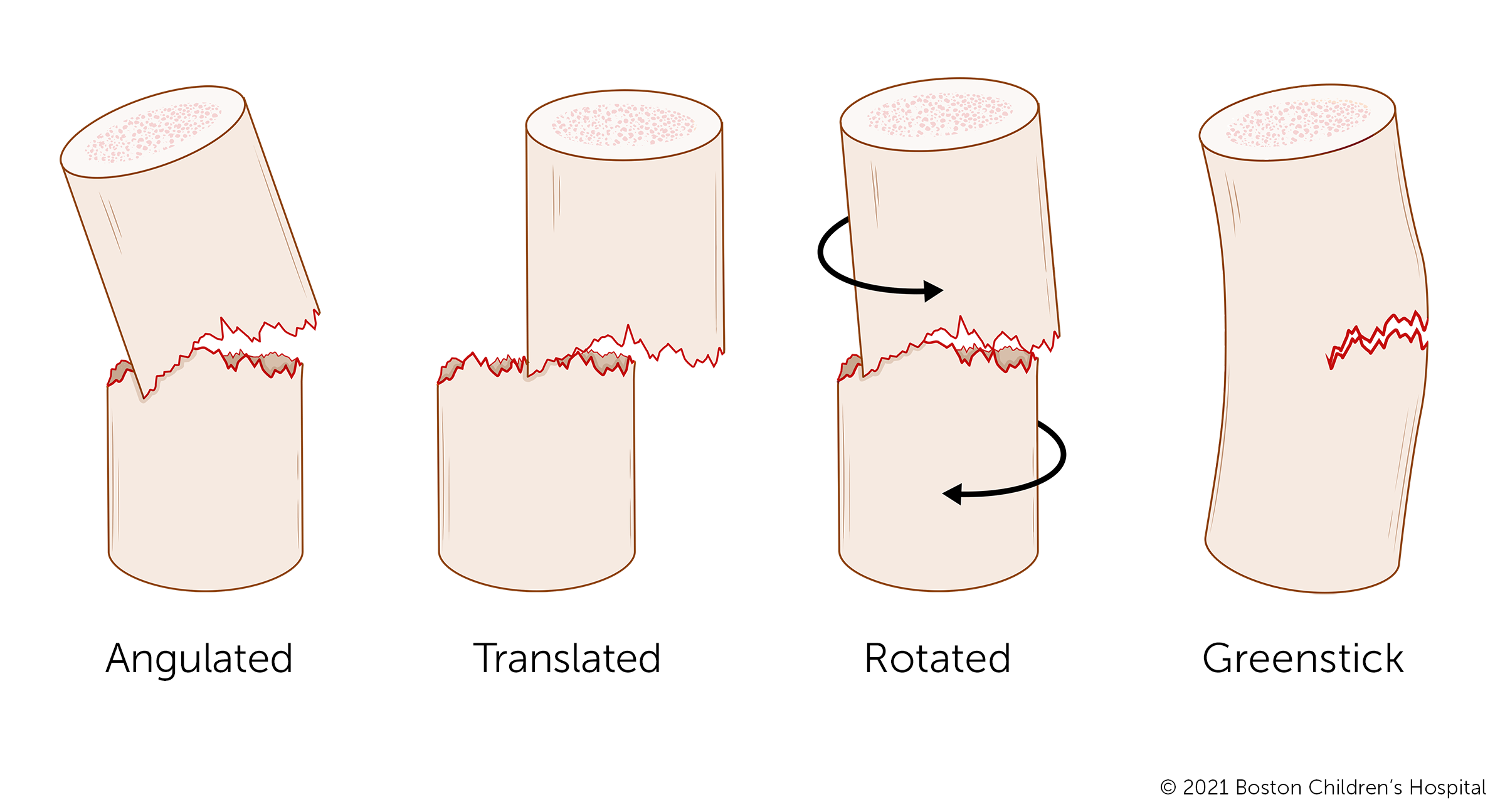
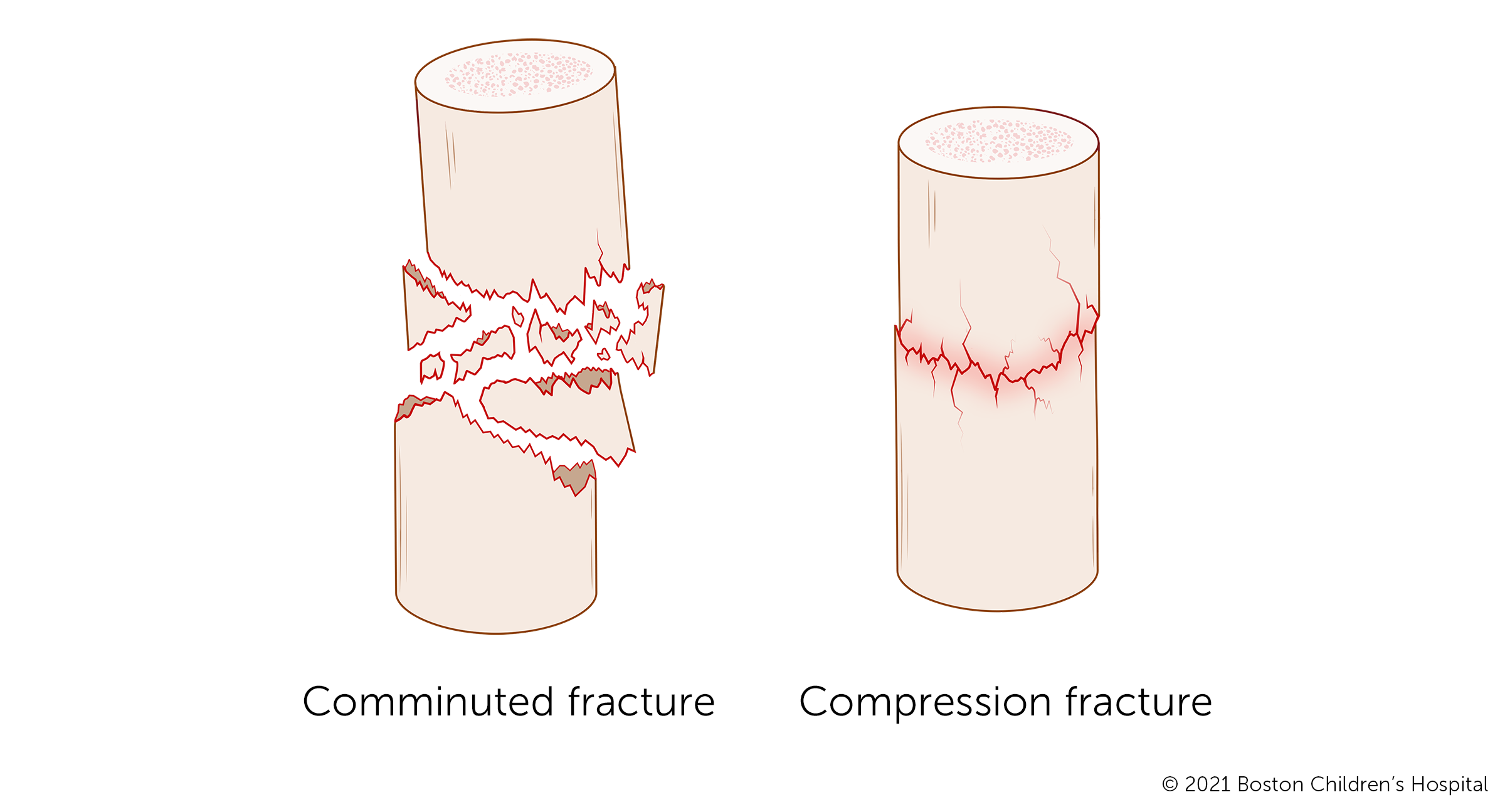
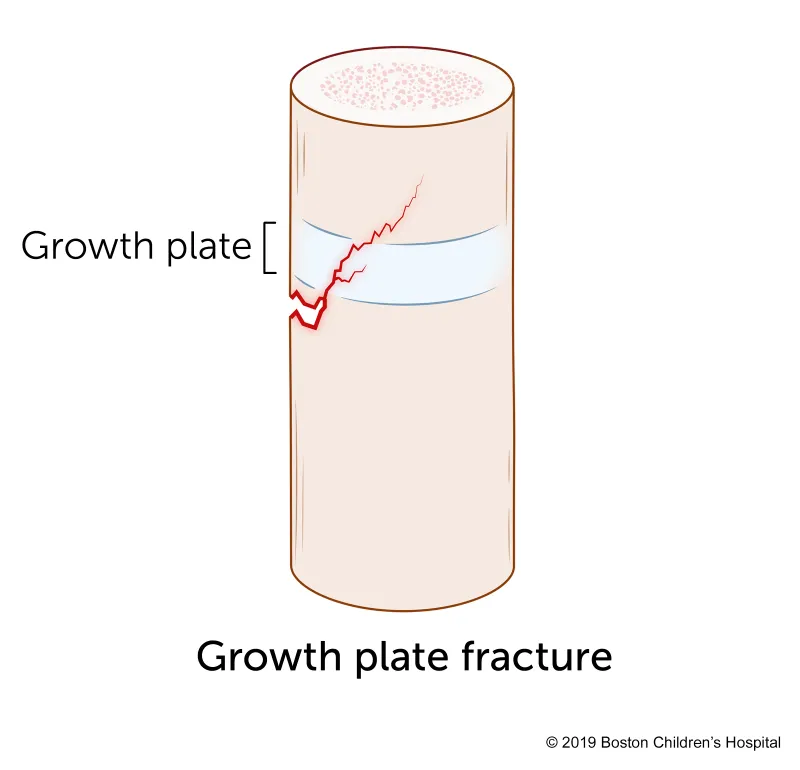
Reduction
A reduction is a non-surgical procedure to set the bone so it will heal properly. The doctor realigns the broken bone from outside the body and puts the injured limb in a cast or splint. Reductions are usually performed in an emergency department with medications that manage pain and make your child sleepy or sedated so they won’t remember the procedure.
Surgery
Severe or unstable fractures that can’t be set properly with a reduction require surgery. To increase the chances that the bone will heal in the correct position, your child's doctor will decide very early in treatment whether to operate. In some cases, however, if the area around the fracture is swollen, the procedure may have to wait until the swelling goes down.
The child will be sedated or under general anesthesia in the operating room and the doctor will set the bone into place. A pin may be used to hold the pieces of bone securely in place while the bone heals. If the fracture involves a joint, the surgeon will realign the joint and hold it in place with screws, a plate, or a pin.
Other treatments
Traction uses a gentle, steady pulling motion in a specific direction to allow the ends of the broken bone to align and heal. In some cases, traction reduces painful muscle spasms.
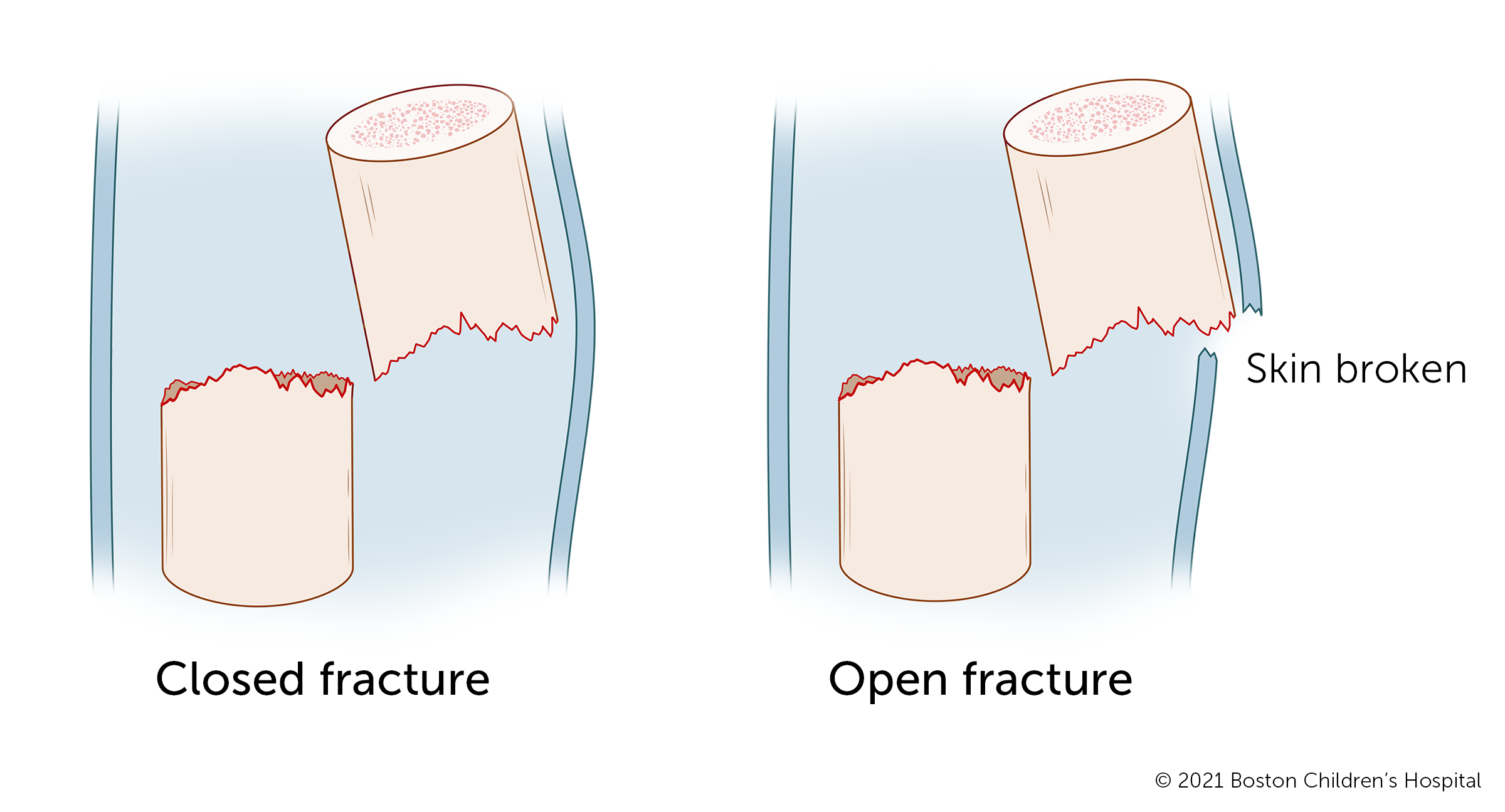
Medication is sometimes used to help control pain and muscle spasms. If a fracture is open, antibiotics are used to prevent infection.